Maths
>
A-Level
>
Probability
>
What is a ...
What is a formula you can use when working out the probability of B given A?
4 years ago
·
15 Replies
·
5666 views
Alysha Wiegand
15 Answers
This is P(AnB)/P(A)
Experienced Maths Teacher (18 yrs) & Examiner for 2 Major Exam Boards
30 reviews
P(B/A) = P(B n A)/P(A)
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.P(B/A)=P(A and B)/P(A)
Probability of B given A = (Probability of A and B) / (Probability of A)
P(B given A)= P(B intersection of A)/P(A)
The formula which we can use to work out this conditional problem is as follows:
Probability(A and B) ➗Probability(A).
Experienced GCSE and A level Maths teacher with 500 hours online
P ( A/B) = P(AnB)/P(B) this is read as probability of A given B is the probability of A and B divided by the probability of B.
If information is represented in a Venn diagram we can also use
P(A/B) = n(AnB) /n(B)
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.
Given that A has occurred we can work out that the probability of B is the probability of A and B occuring divided by the probability of A (the above is the opposite for the probability of A given B). We can work out the probability of A and B by multiplying the Probability of A and the probability of B together (as shown below):
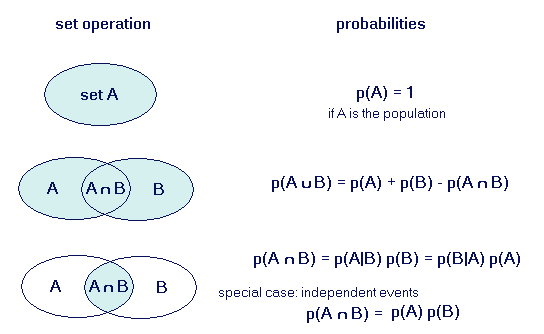
Very experienced A-level Maths & Further Maths teacher
9 reviews
P(B|A) = P(B∩A) / P(A)
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Tutor in Maths and Statistics with 7 years experience including SpLD
3 reviews
When calculating such a probability, you want to use the formula p(B|A) = P(BnA)/P(A)
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Online Tutor for GCSE and A level Mathematics
P(B/A)=P(A and B) / P(A)
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.P(B|A) = [ P(B and A) ] /P(A) = [P(B).P(A|B)] / P(A)
P(B|A)= P(A|B)/P(A)
So conditional probability refers to the chances of event B occurring given that event A has occurred.
The general term for P(B|A)=P(A and B)/P(B)
The faster step will be checking if A and B are independent. (event A has no effect on the change of happening of event B)
If yes, p(B|A)=P(B). If no, P(B|A)=P(A and B)/P(B)
To work put the probability of B given A, usually, you will be given the probabilities of both independent events occurring and the opposite of what you want to work out.
For example:
if P(A) = 0.6,
P(B) = 0.3
and if P(A|B) = 0.45
use the formula P(B|A) = P(A)*P(A|B)
P(B)
then P(B|A) = (0.6)(0.45)
(0.3)
= 0.9
Think you can help?

Need an A-Level Maths tutor?
Get started with a free online introductions with an experienced and qualified online tutor on Sherpa.
Find an A-Level Maths Tutor