Biology
>
GCSE
>
Cells and Control
>
difference...
differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
3 years ago
·
490 Replies
·
33034 views
Elizabeth Dempsey
490 Answers
Qualified teacher, former Head of Chemistry and Examiner.
Prokaryotic cells do not have a DNA enclosed in a nucleus and have no membrane-bound organelles. Whereas, eukaryotic cells have their DNA stored in a nucleus and contain many organelles that have a membrane.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Experienced Science teacher with over 12 years of teaching experience
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have several key differences:
1. Size:
Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller
Eukaryotic cells are larger
2. Nucleus:
Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus; their genetic material is in a nucleoid region.
Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane.
3. Organelles:
Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles (e.g., no mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum).
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, the Golgi apparatus, and the endoplasmic reticulum.
4. Genetic Material:
Prokaryotic cells have a single, circular DNA molecule without histones.
Eukaryotic cells have multiple linear DNA molecules associated with histones.
5. Cell Division:
Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission.
Eukaryotic cells divide by mitosis (and meiosis for reproduction).
6. Ribosomes:
Prokaryotic cells have smaller ribosomes (70S).
Eukaryotic cells have larger ribosomes (80S).
7. Cell Wall:
Prokaryotic cells often have a cell wall made
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Qualified Science teacher with the knowledge to make you succeed
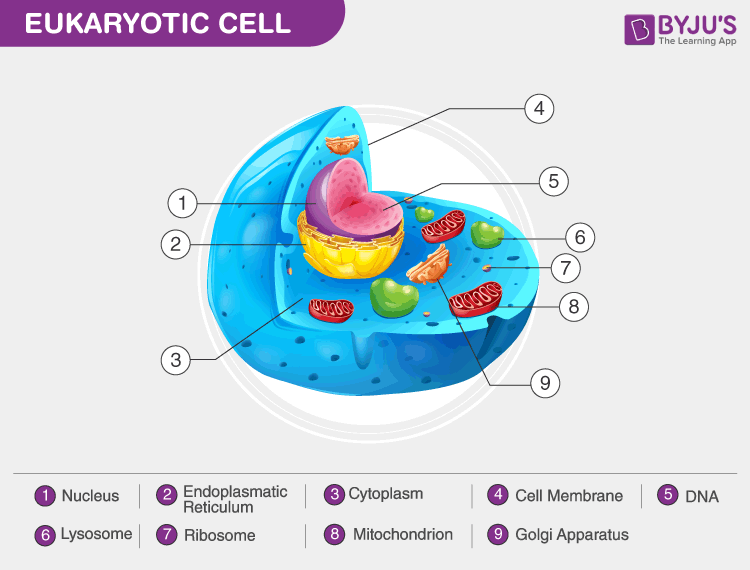
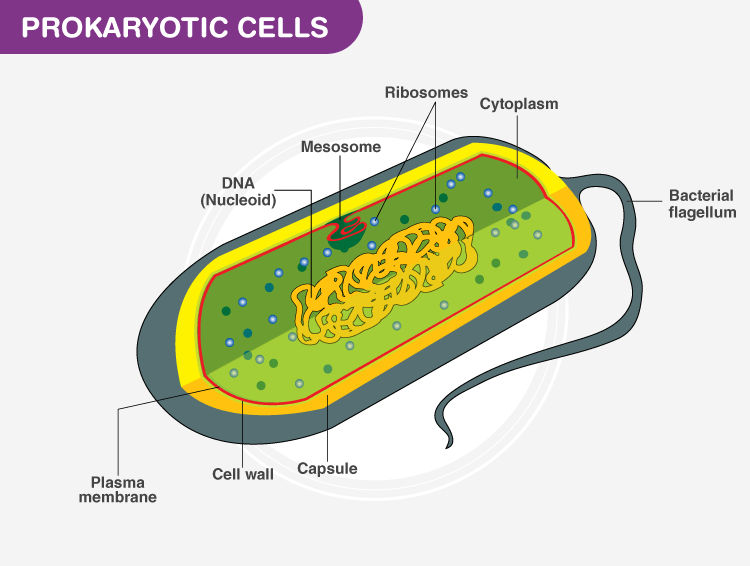
- Cell type: Prokaryotic cells are unicellular, while eukaryotic cells can be unicellular or multicellular.
- Size: Prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells.
- Nucleus: Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus.
- Organelles: Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles.
- DNA: Prokaryotic DNA is circular and non-chromosomal, while eukaryotic DNA is linear and packed into chromosomes.
- Cell membrane: Prokaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, while eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane that is a phospholipid bilayer.
- Transcription: Prokaryotic transcription takes place in the cytoplasm, while eukaryotic transcription takes place in the nucleus.
- Cell division: Prokaryotic cells undergo binary fission, while eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis.
- Locomotion: Prokaryotic cells use flagellin, a hook, and a motor complex to move, while eukaryotic cells use microtubule bundles called flagella.
- Examples: Prokaryotic cells include bacteria and archaea, while eukaryotic cells include plants, animals, fungi, algae, and protozoans.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.⭐Doctor & teacher with 9 years' experience in GCSE & A-Level Biology.
Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, with their DNA free-floating in the cytoplasm. In contrast, eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus and various membrane-bound organelles for specialized functions.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.eukaryotic have a nucleus
eukaryotic have a membrane bound orangells
eukaryotic cells are larger
Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells:
- Size and Structure:
- Prokaryotic Cells are smaller (0.1–5.0 micrometres) and simpler in structure.
- Eukaryotic Cells are larger (10–100 micrometres) and more complex.
- Nucleus:
- Prokaryotic Cells do not have a nucleus. Their DNA is free in the cell in a region called the nucleoid.
- Eukaryotic Cells have a nucleus that contains their DNA.
- Organelles:
- Prokaryotic Cells do not have membrane-bound organelles, like mitochondria or the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Eukaryotic Cells have membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum.
- DNA:
- Prokaryotic Cells have a single, circular DNA molecule.
- Eukaryotic Cells have multiple, linear chromosomes inside the nucleus.
- Cell Wall:
- Prokaryotic Cells usually have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan (in bacteria).
- Eukaryotic Cells may have a cell wall (e.g., in plant cells) made of cellulose; animal cells do not have a cell wall.
- Reproduction:
- Prokaryotic Cells reproduce by binary fission.
- Eukaryotic Cells reproduce by mitosis (asexual reproduction) and meiosis (sexual reproduction).
- Examples:
- Prokaryotic Cells: Bacteria and archaea.
- Eukaryotic Cells: Animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
prokaryotic cells are simple and mostly unicellular and they don't have clear nucleus in their bodies on the other hand the eukaryotic cells which are complex and multicellular and they have clear nucleus in their bodies
Fully qualified Science teacher and highly experienced GCSE Examiner
Prokaryotic cell have no nucleus but Eukaryotic cells have nucleus.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Fully qualified Triple/ Combined Science teacher and GCSE Examiner
10 reviews
For GCSE's you need to remember that Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles such as a nucleus whereas, Prokaryotic cells are do not. Secondly, remember some examples, Eukaryotic cells are plant and animal cells whereas Prokaryotic cells are bacteria cells.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Eukaryotic cells are cells like animal or plant cells.
prokaryotic cells are cells like bacteria.
The key difference between the two is that Eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound organelles whereas prokaryotic cells do not. They also have variable (different) organelles, for example eukaryotic cells have a nucleus whereas prokaryotic cells do not!
Eukaryotic cells have a membrane around the nucleus whereas prokaryotic cells dont
The biggest difference is that a eukaryotic cell (plant/animal/fungus) cell has a nucleus, whereas a prokaryotic (bacterial) cell does not. Prokaryotic genetic material floats freely in the cell cytoplasm.
Aside from that, here are some other key differences:
- Edivide by mitosis (meiosis in gametes), prokaryotes divide by binary fission
- Eukaryotes are 5μm - 100μm, prokaryotes are much smaller (0.2-2μm)
- Prokaryotes don't contain mitochondria or chloroplasts
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the two primary types of cells, differing fundamentally in their structure and complexity. Here are the key differences between them:
- Nucleus:
- Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus. Their genetic material is not enclosed within a nuclear membrane; instead, it is located in a region called the nucleoid.
- Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus, where the cell’s DNA is enclosed within a nuclear envelope.
- Cell Size:
- Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller, typically between 0.1 to 5 micrometers in diameter.
- Eukaryotic cells are larger, usually between 10 to 100 micrometers in diameter.
- Cell Complexity:
- Prokaryotic cells are simpler in structure, with fewer types of organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells are more complex, containing a variety of organelles such as mitochondria, the endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus.
- Cell Wall:
- Many prokaryotes have a rigid cell wall composed of peptidoglycan (in bacteria) or other substances.
- Eukaryotic cells may or may not have a cell wall. If present, the cell wall is usually made of cellulose (in plants) or chitin (in fungi).
- Ribosomes:
- Prokaryotic cells contain 70S ribosomes, which are smaller.
- Eukaryotic cells contain 80S ribosomes, which are larger.
- DNA Structure:
- Prokaryotic DNA is typically circular and not associated with histone proteins.
- Eukaryotic DNA is linear and closely associated with histones to form chromatin and chromosomes.
- Reproduction:
- Prokaryotes reproduce asexually through processes such as binary fission.
- Eukaryotes can reproduce both sexually and asexually, with mechanisms including mitosis and meiosis.
- Organelles:
- Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells have multiple membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, chloroplasts (in plants), the endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus.
- Cytoplasmic Division:
- Prokaryotic cells often divide by binary fission, where the cell simply splits into two.
- Eukaryotic cells divide by mitosis or meiosis, involving complex processes of chromosomal alignment and separation.
- Genetic Recombination:
- Prokaryotic genetic recombination occurs through processes such as transformation, transduction, and conjugation.
- Eukaryotic genetic recombination primarily occurs during meiosis.
These differences reflect the evolutionary distance between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, with eukaryotic cells representing a more complex and compartmentalized cellular organization.
When the student is ready, the teacher will appear!
9 reviews
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus whilst eukaryotic cells do! An easy way to remember this is by telling yourself 'eu' is 'yes' due to the similarly in wording so in essence- eukaryotic yes nucleus!
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Nucleus(DNA):
- Prokaryotic Cells: No nucleus; their genetic material is free-floating in the cell.
- Eukaryotic Cells: Have a nucleus that holds their genetic material.
Size:
- Prokaryotic Cells: Generally smaller and simpler (usually 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers).
- Eukaryotic Cells: Typically larger and more complex (usually 10 to 100 micrometers).
Organelles:
- Prokaryotic Cells: Lack membrane-bound organelles; they have basic structures like ribosomes.
- Eukaryotic Cells: Contain membrane-bound organelles, like mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum, which perform specific functions.
Cell Wall:
- Prokaryotic Cells: Most have a rigid cell wall made of peptidoglycan (in bacteria).
- Eukaryotic Cells: Some (like plants and fungi) have cell walls made of cellulose or chitin, but animal cells do not have cell walls.
Reproduction:
- Prokaryotic Cells: Reproduce asexually, mainly through binary fission (splitting in half).
- Eukaryotic Cells: Can reproduce asexually (mitosis) or sexually (meiosis).
Think you can help?

Need a GCSE Biology tutor?
Get started with a free online introductions with an experienced and qualified online tutor on Sherpa.
Find a GCSE Biology Tutor