Biology
>
GCSE
>
Cells and Control
>
difference...
differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
3 years ago
·
490 Replies
·
33049 views
Elizabeth Dempsey
490 Answers
Warwick Medical Student with 3 years of online tutoring experience.
15 reviews
Cell Structure:
- Prokaryotic cells: They are typically smaller and simpler in structure. They lack a distinct nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Instead, their genetic material, DNA, is found in a single circular molecule called the nucleoid, floating freely in the cytoplasm.
- Eukaryotic cells: These cells are larger and more complex. They have a well-defined nucleus, enclosed by a nuclear membrane, where the DNA is housed. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells contain various membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
Nucleus:
- Prokaryotic cells: Lack a true nucleus. The genetic material is not enclosed within a membrane-bound nucleus.
- Eukaryotic cells: Have a true nucleus, which means the DNA is enclosed within a double-membrane structure, providing greater control over genetic material and cellular processes.
Organelles:
- Prokaryotic cells: Have very few organelles. They contain ribosomes for protein synthesis and may have some specialized structures like the cell wall, plasma membrane, and flagella.
- Eukaryotic cells: Contain a variety of membrane-bound organelles, each with specific functions. For example, mitochondria are involved in energy production, the endoplasmic reticulum is important for protein synthesis and transport, and the Golgi apparatus is involved in modifying and packaging molecules.
Cell Division:
- Prokaryotic cells: Reproduce through binary fission, a simple and rapid process where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
- Eukaryotic cells: Undergo mitosis for growth, development, and tissue repair, as well as meiosis for the production of gametes (sex cells) for sexual reproduction.
Examples of Organisms:
- Prokaryotic cells: Found in unicellular organisms like bacteria and archaea.
- Eukaryotic cells: Found in both unicellular organisms like protists and multicellular organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and some protists.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.A Prokaryotic cell does not have a true, membrane-bound nucleus, unlike a Eukaryotic cell.
Eukaryotic cells have nucleus and have a complex structures with lots of organelles. While prokaryotic cells is simple with no nucleus and no organelles.
Qualified doctor with more than half a decade experience teaching science
2 reviews
Eukaryotic Cells have their DNA contained in a nucleus, Prokaryotic Cells do not have an organised nucleus.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Undergraduate studying Biochemistry at the University of Oxford.
2 reviews
Prokaryotic cells lack a defined nucleus whereas eukaryotic cells have one. The genetic material in prokaryotic cells is circular, whereas in eukaryotes it is linear. Prokaryotes also do not have membrane bound organelles and they are almost always unicellular. In contrast, eukaryotic cells can be either multicellular or unicellular; eukaryotic cells are much more complex. Prokaryotes divide by binary fission whereas eukaryotes divide through mitosis.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Friendly Oxford Medical Student with 2+ years Tutoring experience
Prokaryotic cells can be distinguished from eukaryotic cells as they lack a nucleus (and also lack any other membrane-bound organelles). Therefore prokaryotic DNA is free in the cytoplasm, whereas the DNA of eukaryotic cells is enclosed in a nucleus.
Prokaryotic cells also have different types of DNA to eukaryotic cells: while both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain DNA arranged in chromosomes, prokaryotic cells may additionally contain plasmid DNA (a circular loop of DNA which is separate from chromosomal DNA).
It is important to note that forming single-celled organisms is NOT specific to prokaryotic cells - eukaryotic cells can also form single celled organisms (e.g. amoeba). This is something I didn't initially realise at GCSE!
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Great question! The easiest way to think about it is this:
Prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) are simpler and smaller. They don’t have a nucleus—instead, their DNA floats freely in the cell. They also don’t have membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria or chloroplasts. Think of them as the “basic” version of a cell.
Eukaryotic cells (like animal and plant cells) are more complex and larger. They do have a nucleus that stores their DNA, and they have lots of organelles, like mitochondria (which make energy) and, in plant cells, chloroplasts (which do photosynthesis).
So in short:
- Nucleus? Only in eukaryotic cells
- Size? Eukaryotic cells are bigger
- Organelles? Eukaryotic cells have them, prokaryotic don’t
- Examples? Prokaryotes = bacteria | Eukaryotes = animals, plants, fungi
Hope that helps make things clearer!
Qualified Science teacher with the knowledge to make you succeed
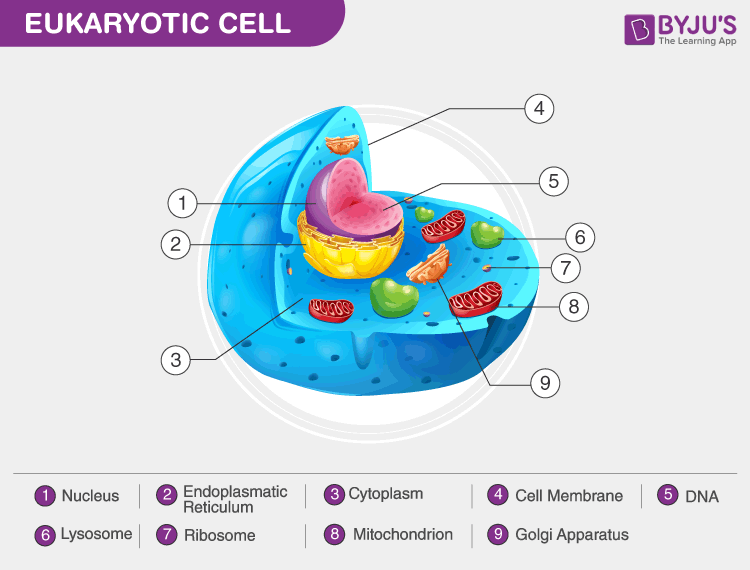
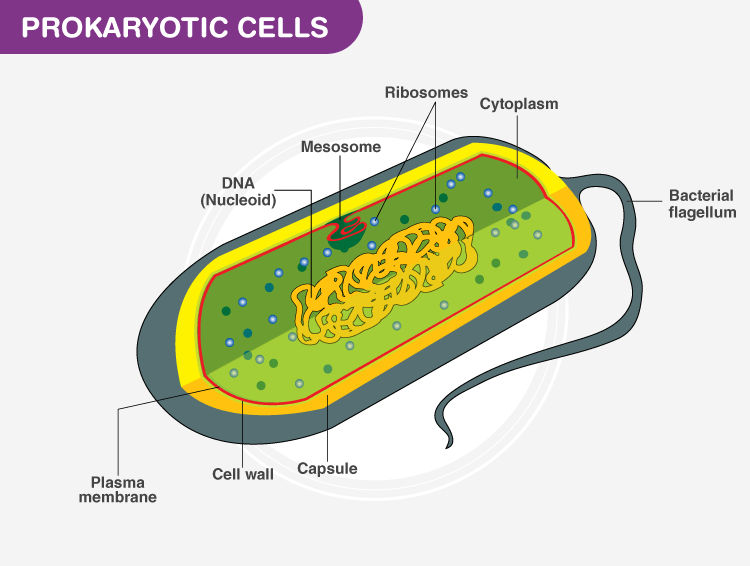
- Cell type: Prokaryotic cells are unicellular, while eukaryotic cells can be unicellular or multicellular.
- Size: Prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells.
- Nucleus: Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus.
- Organelles: Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles.
- DNA: Prokaryotic DNA is circular and non-chromosomal, while eukaryotic DNA is linear and packed into chromosomes.
- Cell membrane: Prokaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, while eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane that is a phospholipid bilayer.
- Transcription: Prokaryotic transcription takes place in the cytoplasm, while eukaryotic transcription takes place in the nucleus.
- Cell division: Prokaryotic cells undergo binary fission, while eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis.
- Locomotion: Prokaryotic cells use flagellin, a hook, and a motor complex to move, while eukaryotic cells use microtubule bundles called flagella.
- Examples: Prokaryotic cells include bacteria and archaea, while eukaryotic cells include plants, animals, fungi, algae, and protozoans.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.eukaryotic cells are plant and animals cells and are distinguishable because they have a nucleus,
Prokaryotic cells are bacterial cells and are distinguishable because they have free flowing DNA as well and Plasmids
Prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Examples are bacteria and archaea. In contrast, eukaryotic cells are more complex with membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. In contrast, eukaryotic cells are more complex and contain membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Examples are plant and animal cells.
Experienced tutor of over 3 years, all subjects and ages!
19 reviews
Hi Elizabeth, heres a short summary on the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
Nucleus:
- Prokaryotic cells: No nucleus; DNA is free-floating in the cytoplasm.
- Eukaryotic cells: Has a nucleus where DNA is enclosed.
- Size:
- Prokaryotic cells: Generally smaller (0.1-5.0 µm).
- Eukaryotic cells: Generally larger (10-100 µm).
- Cell Structure:
- Prokaryotic cells: Simple structure; no membrane-bound organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells: Complex structure; has membrane-bound organelles (e.g., mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum).
- DNA Shape:
- Prokaryotic cells: Circular DNA.
- Eukaryotic cells: Linear DNA organized into chromosomes.
- Ribosomes:
- Prokaryotic cells: Smaller ribosomes (70S).
- Eukaryotic cells: Larger ribosomes (80S).
- Examples:
- Prokaryotic cells: Bacteria and Archaea.
- Eukaryotic cells: Animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.⭐️⭐️LIVE⭐️⭐️ availability .. need last minute help on a topic? panicking before Mocks? Let me help you get unstuck ..
8 reviews
In simplistic terms, Prokaryotes are much simpler and are usually single cells. Prokaryotes include bacteria. They do not contain organelles that have a membrane around them, such as a nucleus and mitochondria. Eukaryotic cells on the other hand are more complex and include plant and animal cells.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.tutor offering maths, science + english. KS3+
4 reviews
Prokaryotic Cells:
- Lack a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- Genetic material is typically found in the nucleoid region.
- Generally smaller and simpler in structure.
- DNA is typically a single, circular chromosome.
- Lack membrane-bound organelles except for some specialized structures like ribosomes.
- Have a cell wall outside the plasma membrane, often composed of peptidoglycan.
- Reproduce primarily through binary fission.
Eukaryotic Cells:
- Have a true nucleus enclosed within a nuclear membrane.
- Genetic material is organized into multiple linear chromosomes within the nucleus.
- Typically larger and more complex, with various membrane-bound organelles.
- DNA is organised into multiple linear chromosomes.
- Contain membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus.
- Plant cells have a cell wall composed of cellulose, while fungal cells have a cell wall made of chitin.
- Reproduce via mitosis for growth and meiosis for sexual reproduction.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Eukaryotic cells are complex cells that contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are found in multicellular organisms such as animals, plants, and fungi. Prokaryotic cells are simple cells that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are found in single-celled organisms such as bacteria.
Experienced Science teacher, Examiner and Assistant Headteacher
2 reviews
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, prokaryotic cells do not.
Eukaryotic examples are animal and plant cells
Prokaryotic example would be bacterial cell
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Think you can help?

Need a GCSE Biology tutor?
Get started with a free online introductions with an experienced and qualified online tutor on Sherpa.
Find a GCSE Biology Tutor