Maths
>
GCSE
>
Rates of Change
>
How do you...
How do you find the rate of change?
3 years ago
·
215 Replies
·
16811 views
Vickie Shanahan
215 Answers
The rate of change can be found on a straight-line graph by selecting two coordinates and dividing the change in the y-values by the change in the x-values. This can be shown in the formula : m = y2-y1/ x2-x1 with m representing the gradient of the straight-line. Additionally, x and y can be two different variables and the formula is used to calculate average speed or average velocity.The rate of change of a straight line is equivalent to the gradient of a straight line graph. However, we use differentiation with non-linear graphs to find the rate of change at a particular point. This is another topic in itself.
Frays of change is how much x. Ganges w time or another variable . So this can be done by working out the gradient of a graph or differentiating If it is an expression
Teaching Math, Physics and Chemistry for over 10 years!
12 reviews
Hi Vickie,
The rate of change is usually obtained if you divide by time.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Derivatives are the best tool, but not for everyone... Considering two variables (distance and time, for example), you can also take the first and last value of both in a certain process, subtract the ones from the same variable (e.g. last and first distances of the bus from your position) and divide the subtractions of different variables. By doing this with position/distance and time, the rate of change you get is the speed of the object you're analyzing!
There are a couple of ways to find this. If your data is displayed in graph format, you can find the rate of change by dividing the change in y-values by the change in x-values. If you are talking about the instantaneous rate of change (this is called the derivative of a function) then we need to look further at the function itself.
Hello Mrs Vickie Shanahan. There isn't much context to your question here, so I'll keep my response as general as possible:
The rate of change describes a relationship between a dependent and an independent variable. For example, the rate of change of velocity with time or the rate of change of temperature with distance.
In a simple mathematical case, we'd write this as the change in the dependent variable (temperature, dT) over a fixed interval of the independent variable (distance, dx)
Which is mathematically written as dT/dx, or as shown in the graph, dy/dx.
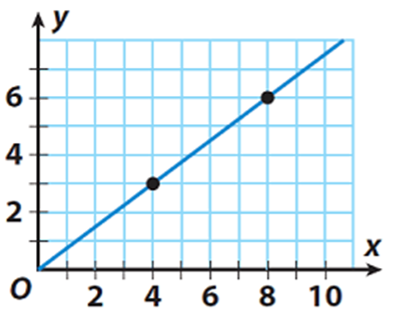
It is then clear that for the linear relationship in the above graph, the rate of change is dy/dx = (y1-y2)/(x2-x1) = (6-3)/(8-4).
Rate of change= gradient
In a linear equation, gradient= y1 – y2 / x1 – x2
In a quadratic equation, gradient = dy/dx.
For a linear set of values the rate of change will be the change in y-values divided by the change in x-values in other words the gradient of a straight line. In the set of values relating to a curved line the rate of change on each point can be found by differentiating the equation of that curve and using the values of x of the point you need to find the rate of change at.
Referring to a straight line graph, the rate of change can be found using the formula: change in y/change in x, practically speaking, When dealing with a straight line, it's best to "make a right angled triangle" choosing points appropriately. Your result is the "gradient" or "slope" of the line which tells you the rate of change. It can either be positive, negative or 0 if the straight line is parallel to the x axis.
The rate of change on a line graph is called the gradient and is calculated by the change in y axis/ change in x axis. What this means is that you find 2 points on the line and find the difference between the y coordinates and divide that by the difference in x axis.
To find the rate of change of something you calculate how much the “something” has changed by and then divide it by the number of seconds that have passed.
By finding the gradient of the line. You can do this by using the formula: m = (y2 — y1) / (x2 — x1). Where m is the gradient.
Rate of change can be calculated by the amount of a specific quantity is changing by the time it took for the change to hapen. A common example in physics in speed which is simply rate of change of position(or distance). If a car changes its position by 20 miles in 30 minnutes then its average speed(or rate of change of position) is 20miles divided by 30min(or 0.5 hr) which is 40 miles per hr
Your bridge to Maths & Physics success. Let's ace it together!
5 reviews
The rate of change can be found by calculating the difference in the values of a quantity over a certain period of time or another variable. It is often calculated using the formula:
Rate of change = (Change in quantity) / (Change in time or another variable)
For example, to find the rate of change of distance with respect to time, you would divide the change in distance by the change in time. This gives you the speed or velocity.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Experienced Physics and Mathematics tutor from beginner to degree
The Rate of change (ROC) is the increase or decrease of one value related to another value.
The speed of a car for instance is the distance covered divided by the time taken.
In mathematics this can be the gradient of a graph in general terms.
I'm available for 1:1 private online tuition!
Click here to view my profile and arrange a free introduction.Think you can help?

Need a GCSE Maths tutor?
Get started with a free online introductions with an experienced and qualified online tutor on Sherpa.
Find a GCSE Maths Tutor